No trader steps into the financial markets to watch their hard-earned capital dissipate. Yet, the harsh reality is that losses are an inherent part of the trading journey. To minimize your losses and increase your profits, a robust risk management strategy is necessary. Without it, the potential for costly errors looms large, casting a shadow on your capital. So, what is risk management?
In this guide, we will answer this question and teach you how to develop a solid risk management plan, as well as introduce you to a wide array of risk management tools used by professional traders. Let’s get started!
What Is Risk Management?
Risk management in trading refers to identifying, evaluating, and mitigating risks of potential losses to protect your investments and pave the way for long-term growth. It ensures that any negative impact of a trade is manageable and a desirable risk/reward ratio is maintained.
Here’s what you need to do to minimize risks and increase trading gains:
- Identify potential risks.
- Develop a detailed risk management plan. This means implementing a set of rules and measures to effectively mitigate risks and remain profitable in the long run.
- Stick to your plan.
A risk management plan is based on your risk tolerance and investment goals. It establishes clear guidelines on the percentage of total capital to risk on a single trade and defines the risk-reward ratio. The risk-reward ratio is a key metric that ensures your potential gains outweigh potential losses. A well-designed plan gives traders a significant edge.
As the saying goes, “You need to plan the trade and trade the plan”. This includes having a well-thought-out risk management strategy and executing it consistently.
The strategy must establish your entry and exit points and position size to help you trade per your plan and keep emotions at bay.
Risk Management Tools and Techniques
Now that we’ve explored the question “What is risk management,” it’s time to discuss the best risk management tools and techniques to help you get geared for success.
The 1% Rule
The 1% rule in risk management suggests risking no more than 1% of your total trading capital on a single trade. This means that if you have a total trading capital of $10,000, you should not risk more than $100 on a single trade.
Start by assessing the total amount of money you want to invest in the market. Then calculate 1% of that amount. Use the 1% risk amount to determine how much of the asset you can afford to trade while staying within the risk limit.
Of course, the investment amount may vary depending on the trading strategy that you choose. While some traders prefer to increase the number to 2%, the 1% approach is considered more conservative. Regardless of what you choose, 1 or 2 percent, there is a stark difference between 1% and 10%. By taking small risks, you avoid factors that can be detrimental to your long-term profits, and you don’t put a large part of your capital at risk.
Risk-Reward Ratio
The risk-reward ratio is a crucial metric in risk management that quantifies the potential gain versus potential loss in a given trade. It represents the relationship between the amount of money you’re willing to risk (potential loss) and the potential profit you aim to gain from a trade.
Each trader has to decide on the acceptable risk-reward ratio that they can be comfortable with, and never go beyond that limit. For example, a risk-reward ratio of 1:2 means that for every unit of risk, you anticipate a potential reward of 2 units.
The ideal risk/reward ratio that most traders aim for is 1:2 or even 1:3. For example, let’s consider you want to buy shares of a company that is trading at $50 per share. Your stop-loss level is $48 per share. Your risk will then be $2 per share. As you aim for a profit target that is twice the amount of your risk, your reward will be $4 per share. This way, you will stick to the 1:2 risk-reward ratio.
Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Orders
Stop-loss and take-profit orders are essential risk management tools in a trader’s toolkit, helping manage risk and execute trades at desired price levels.
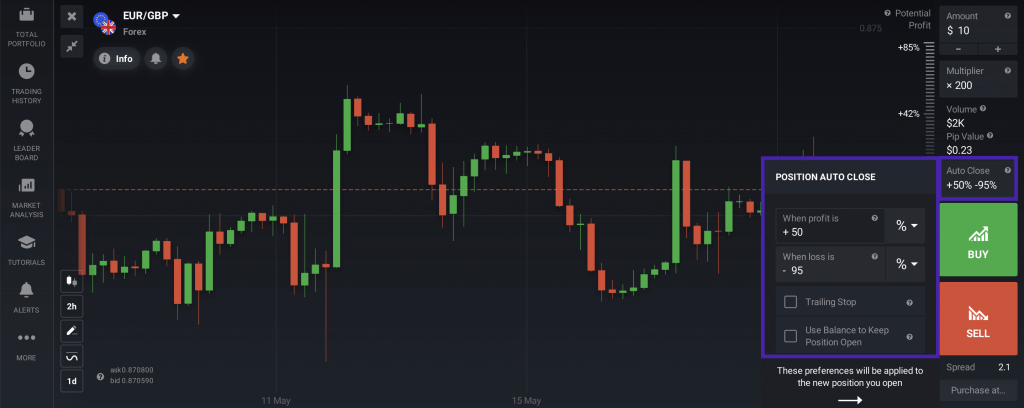
Using a stop-loss order, you can decide on the maximum risk you’re willing to take on and close the position when it reaches a specified price. A stop-loss order automatically closes the position when its price falls to a predetermined level, limiting potential losses. It acts as a safety net, keeping emotions in check and helping traders protect their capital by setting a point where an unprofitable trade is cut short.
A take-profit order helps you get out of a trade when the profit is made and avoid risking a potential market downturn. Once a security’s take-profit level is reached, the trade is automatically closed. If the take-profit level is not reached, the trade will remain open until it does, or until the trader closes it manually, unless it reaches the stop-loss level first.
You can use technical analysis tools such as Support and Resistance, Moving Averages, or Fibonacci Retracement to decide stop-loss and take-profit placement.
If you want to learn more about stop-loss and take-profit features, and find out how to set them up in the traderom, check out the article Level Up Your Trading with Stop-Loss and Take-Profit.
Hedging
Hedging is a popular risk management approach that involves making a second investment to offset potential losses in the first one. In CFD trading, this would mean opening both long and short positions on the same asset. The goal is for the profit from one position to offset at least part of the loss from another.
For example, if a trader opens a “Buy” position on Forex, they can hedge the risks by opening another trade with the same investment amount in the opposite direction by clicking “Sell”. This way the profit for one trade will at least partially cover for the loss from the other trade. It is important to understand that hedging can lower the overall profit from trading, which is why traders who execute this approach need to be careful and stick to their trading plan.
Conclusion
A well-crafted risk management plan, coupled with strategic tools, is key to unlocking sustainable success. So, whether you’re just starting out or looking to refine your strategy, you can manage potential risks by implementing these practices. Remember, however, that there is no risk management tool that can guarantee complete protection from price fluctuations and potential losses.
Note however, that customization is key. Traders often tailor risk management techniques to align with their unique trading strategies, prevailing market conditions, and individual risk tolerance levels.